Introduction to Crawling and Indexing in SEO
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)? and is it backbone of online visibility in 2025. Central to its foundation are two core processes: crawling and indexing. For corporate marketing teams, eCommerce founders, SaaS platforms, and digital agencies, understanding these mechanisms is essential for driving consistent search traffic and achieving ranking dominance.
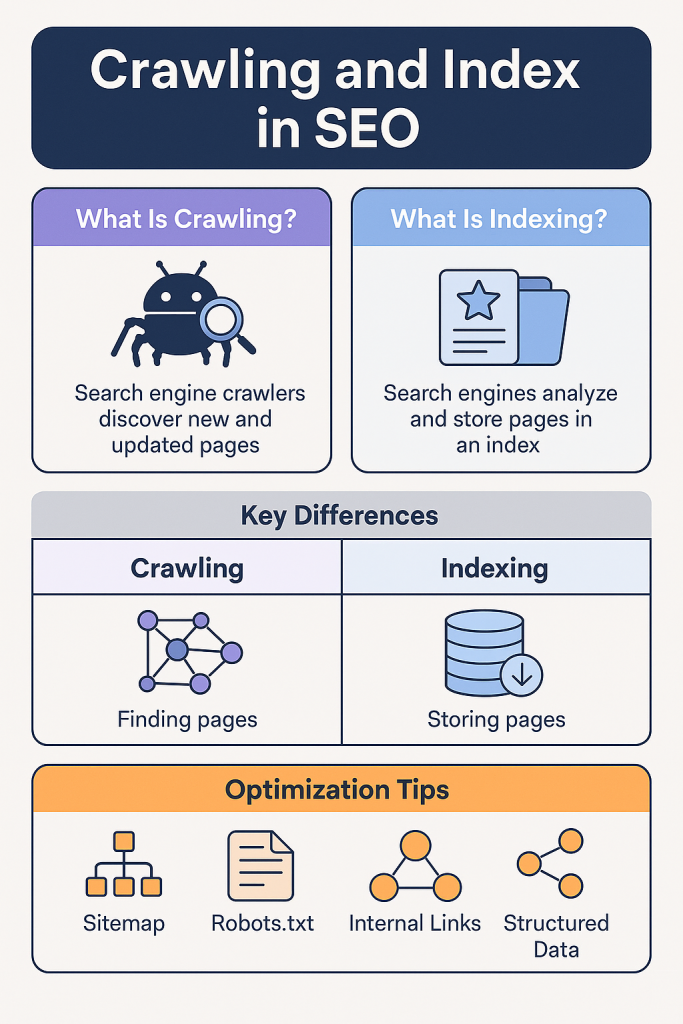
What is Crawling and Indexing in SEO? Crawling refers to the discovery of your web pages by search engine bots, primarily Googlebot. Indexing involves storing and organizing your web content in Google’s massive database so that it appears in search results.
According to Search Engine Journal, over 90% of online experiences begin with a search engine, but only 5.7% of pages rank in the top 10 search results within a year of publication (Ahrefs). Why? Mostly due to poor crawling and indexing setups.
Let’s explore in detail.
What is Crawling in SEO?
Understanding How Googlebot Works
Crawling is the process by which search engines discover new or updated pages on the internet. Google uses a web crawler called Googlebot, which uses a queue of URLs to systematically access and scan content.
- Crawlers: Bots (like Googlebot) access a site and follow links to discover other pages.
- Seed URLs: The process starts with a list of known URLs. Googlebot expands its reach by discovering new pages through links.
- Content Fetching: The crawler retrieves HTML, JavaScript, images, etc.
According to Google Search Central, Googlebot uses over 200 signals to prioritize crawling.
What is Crawl Budget?
Crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot is willing or able to crawl on your site. It depends on two main factors:
- Crawl rate limit: How much crawling Googlebot can do without overloading your servers.
- Crawl demand: The popularity of your pages and how frequently they’re updated.
Best Practices to Improve Crawl Budget:
- Reduce duplicate content.
- Improve server performance.
- Fix broken links (404s).
- Use structured internal linking.
Tools to Monitor Crawling:
- Google Search Console > Crawl Stats
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Ahrefs Site Audit
What is Indexing in SEO?
Indexing is the next step after crawling. Once your site is crawled, its content is stored and categorized in Google’s index.
How Indexing Works:
- Google processes the crawled data.
- It evaluates page quality, relevance, structured data, and duplicate content.
- Indexing decides whether a page is worthy of being shown in search results.
Indexable Content Must Be:
- Accessible (no blocked content via robots.txt)
- Valuable (unique, high-quality content)
- Structured (HTML tags, schema markup, etc.)
A Moz study found that over 30% of submitted pages are never indexed due to thin or duplicate content.
Indexing Triggers:
- Submitting a sitemap
- Internal/external linking
- Social shares and backlink signals
Key Differences Between Crawling and Indexing
| Feature | Crawling | Indexing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Discover pages | Store and rank pages |
| Tool | Googlebot | Search index database |
| Controlled by | Robots.txt, internal links | Meta tags, canonical, content quality |
| Outcome | Page seen by bot | Page eligible to rank |
How to Optimize Your Site for Crawling
1. Use Sitemaps
Submit an XML sitemap via Google Search Console. It provides Googlebot with a roadmap of your site.
2. Configure robots.txt
This file tells bots which pages to crawl and which to avoid.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private/
Allow: /3. Use Internal Linking
Links help bots navigate your site.
- Use contextual anchor text
- Avoid orphan pages
4. Reduce Crawl Errors
Fix 404s, redirect chains, and broken links using tools like:
- Ahrefs
- SEMrush
- Google Search Console
How to Improve Indexing
1. Focus on Content Quality
High-quality content gets indexed faster. Avoid:
- Duplicate content
- Thin pages (under 300 words)
- AI-generated junk
2. Use Canonical Tags
Prevent duplicate content by specifying canonical versions:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yourdomain.com/main-page/" />3. Structured Data Markup
Add schema.org to guide Google:
- Product schema
- Article schema
- Local business schema
4. Avoid Noindex Tags
Double-check meta robots settings:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex"> <!-- Avoid this unless intentional -->Common Crawl and Indexing Issues
1. Duplicate Content
- Causes split link equity
- Confuses Googlebot
- Fix with canonicalization or content consolidation
2. Crawl Errors
Types:
- DNS errors
- Server errors (5xx)
- Not found (404)
3. Blocked Pages
Check robots.txt and noindex in meta tags.
4. Indexing Bugs in JS-heavy Sites
Use pre-rendering or dynamic rendering for single-page apps.
Google Search Console: Your SEO Lifeline
Features:
- URL inspection tool (test live indexing status)
- Sitemap submission
- Crawl stats (errors, fetch frequency)
- Coverage reports (indexed, excluded, errors)
In 2024, Google Search Console received updates to better surface JavaScript-rendered indexing errors.
Pro Tip:
Use the “Request Indexing” feature to manually push updates.
AI’s Role in Crawling and Indexing in 2025
With the rise of machine learning, AI is now guiding Googlebot’s behavior.
Smart Crawling:
- AI predicts which pages are worth crawling more often.
- Low-performing URLs may get crawled less.
NLP in Indexing:
- Google uses BERT and MUM to understand context and intent.
- Pages with semantic structure perform better.
2025 reports from Search Engine Land show that NLP-backed indexing has increased snippet diversity by 40%.
Best Practices for Tech SEO Teams and Marketers
- Conduct Monthly Crawl Audits
- Fix Crawl Depth Issues – Keep important pages within 3 clicks from the homepage
- Update Sitemaps Regularly
- Use Log File Analysis – Understand how bots navigate your site
- Enable Structured Data for All Indexable Pages
- Avoid Chain Redirects – Limit redirects to 1 hop
FAQs
What is crawling in SEO?
Crawling is the process where search engine bots discover pages by following links and sitemaps.
What is indexing in SEO?
Indexing is storing and ranking your content in search engine databases.
How can I check if my site is indexed?
Use Google Search Console or search site:yourdomain.com in Google.
Why is my page not indexed?
Check for noindex tags, thin content, crawl errors, or blocking in robots.txt.
What is crawl budget in SEO?
It’s the number of URLs Googlebot will crawl in a given time. Optimize by improving site performance and content quality.
Final Thoughts
Crawling and indexing in SEO are the gateways to organic traffic. Without them, your site won’t exist in Google’s world. In 2025, with AI-enhanced bots and advanced indexing algorithms, technical SEO is more important than ever.
🔧 Need expert help fixing crawl or indexing issues? AdRankLab offers enterprise-grade technical SEO audits, consulting, and implementation. Let’s get your website fully indexed and optimized!



3 thoughts on “What is Crawling and Indexing in SEO?”